Kia Stinger: Emission Control System
Kia Stinger CK 2018-2025 Service Manual / Emission Control System
Components and components location
| Components Location |
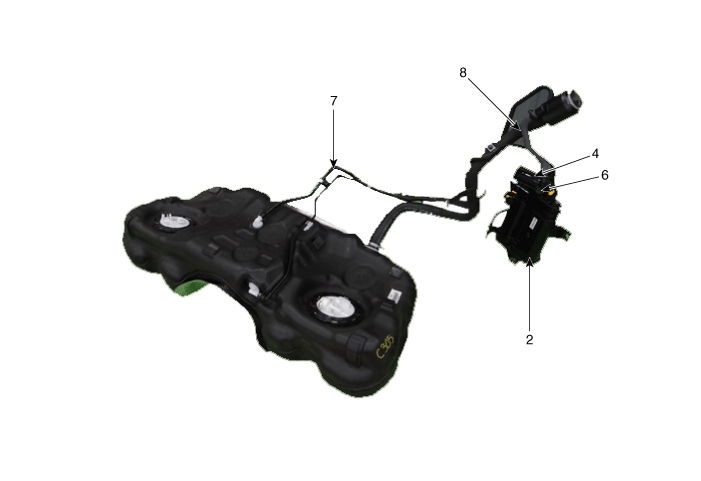
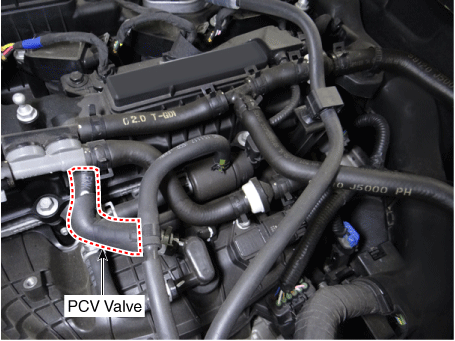
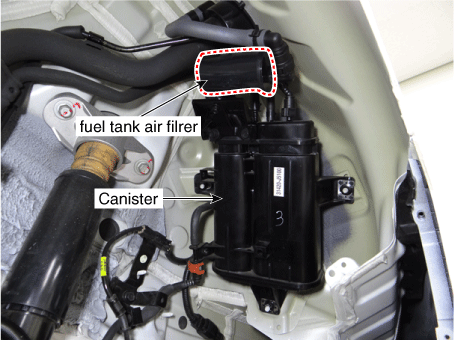
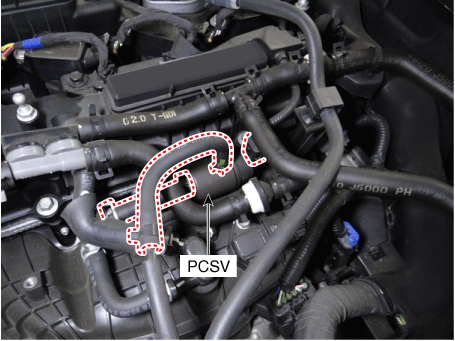
| 1. PCV Valve 2. Canister 3. Purge control solenoid valve (PCSV) 4. Fuel tank air filter |
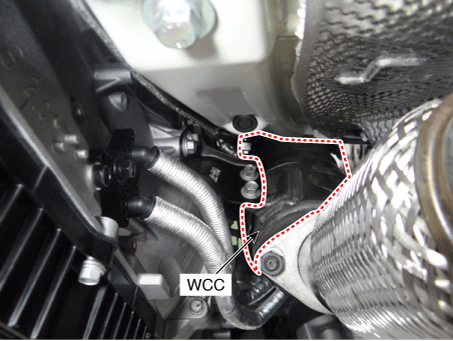
5. Catalytic converter (WCC)
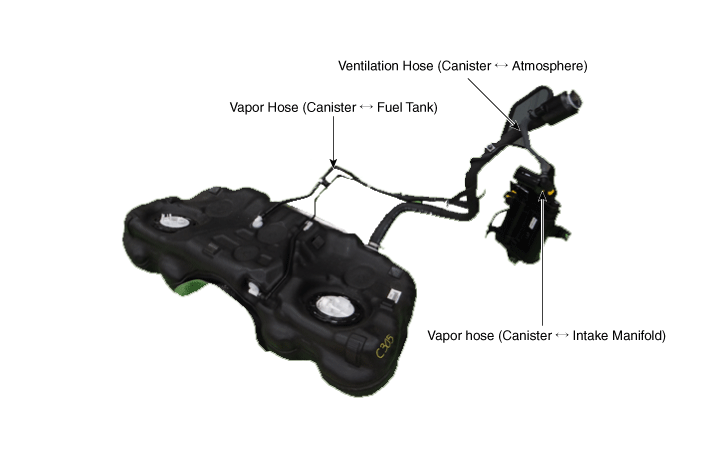
6. Vapor hose (Canister ↔ Intake Manifold) 7. Vapor Hose (Canister ↔ Fuel Tank) 8. Ventilation Hose (Canister ↔ Atmosphere) |
|
1. PCV valve |
2. Canister 4. Fuel tank air filter |
|
|
|
|
3. Purge control solenoid valve (PCSV) |
5. catalytic converter (WCC) |
|
|
|
|
6. Vapor hose (Canister ↔ Intake Manifold) 7. Vapor Hose (Canister ↔ Fuel Tank) 8. Ventilation Hose (Canister ↔ Atmosphere) |
|
|
|
|
Description and operation
| Description |
Emissions Control System consists of three major systems.
| • |
The Crankcase Emission Control System prevents blow-by gas from releasing into the atmosphere. This system recycles gas back into the intake manifold (Closed Crankcase Ventilation Type). |
| • |
The Evaporative Emission Control System prevents evaporative gas from releasing into the atmosphere. This system burns gas at appropriate engine operating condition after gathering it in the canister. |
| • |
The Exhaust Emission Control System converts the three pollutants [hydrocarbons (HC), carbon monoxide (CO), and oxides of nitrogen (NOx)] into harmless substances by using the 3-way catalytic converter. |
Schematic diagrams
| Schematic Diagram |
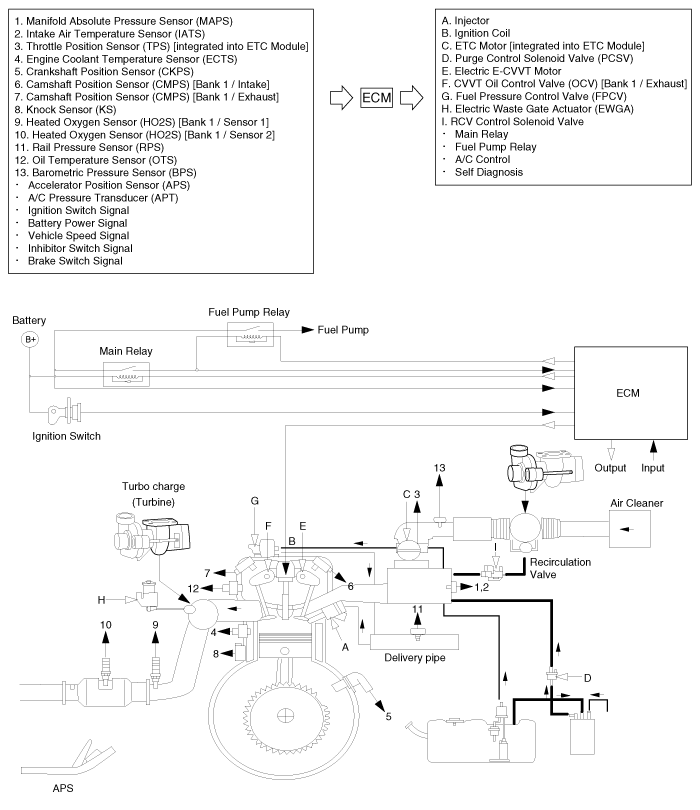
Troubleshooting
| Troubleshooting |
|
Symptom |
Suspected area |
|
Engine does not start or struggles to start |
Vapor hose damaged or disconnected |
|
Engine struggles to start |
Malfunctioning Purge Control Solenoid Valve |
|
Rough idle or engine stalls |
Vapor hose damaged or disconnected |
|
Malfunctioning PCV valve |
|
|
Rough idle |
Malfunctioning Evaporative Emission Control System |
|
Excessive oil consumption |
Positive crankcase ventilation line clogged |
- Specifications
- Crankcase Emission Control System
- Evaporative Emission Control System
- Exhaust Emission Control System
 Smart Cruise Control (Stop & Go) (SCC) ECU
Smart Cruise Control (Stop & Go) (SCC) ECU
Description and operation
Description
The smart cruise control unit is installed on the front right-hand side of the
chassis. A radar sensor is embedded in the front section of the uni ...
 Specifications
Specifications
Service data
Service Data
Purge Control Solenoid Valve (PCSV)
▷ Specification
Item
Specification
Coil Resistance (Ω)
18.5 - ...
Other information:
Kia Stinger CK 2018-2025 Service Manual: Engine Control Module (ECM)
Schematic diagrams ECM Terminal And Input/Output signal ECM Terminal Function Connector [A] Terminal Description Connected to 1 - 2 - ...
Kia Stinger CK 2018-2025 Service Manual: Pillar Garnish
Repair procedures Replacement • Use a plastic panel removal tool to remove interior trim pieces without marring the surface. • Take care not ...
Copyright © www.kstinger.com 2015-2025