Kia Stinger CK: Forward Collision-avoidance Assist (FCA) / FCA warning message and system control
Kia Stinger (CK) 2018-2023 Owner's Manual / Driving your vehicle / Forward Collision-avoidance Assist (FCA) / FCA warning message and system control
Contents:
The FCA system produces warning messages, warning alarms, and emergency braking based on the level of risk of a frontal collision, such as when a vehicle ahead suddenly brakes, or when the system detects that a collision with a pedestrian is imminent.
Collision Warning (1st warning)

- The warning message appears on the LCD display with the warning alarms.
- The FCA controls the brakes within certain limit to reduce the impact from the collision.
Emergency braking (2nd warning)
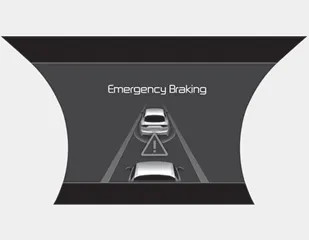
- The warning message appears on the LCD display with the warning alarms.
- The FCA controls the brakes within certain limit to reduce the impact from the collision. The FCA controls the maximum brakes just before the collision.
Other information:
Kia Stinger (CK) 2018-2023 Owner's Manual: Automatic Transmission Control System
Description and operation Description Automatic transmission control system relies on various measurements to determine the current control status and determine the necessary compensation values. These values are used to control the actuators and achieve the desired control output. Control System Composition Shift By Wire (SBW) System Composition ▶ Operating Principle – Instead of cable, the system uses electronic signals to shift between the P-R-N-D gears.Specifications Specification Item Specification Coil Resistance (Ω) 1.4 - 1.6 [20°C(68°F)] Description and operation Description The GDI injector is similar to a standard injector, but sprays fuel at a much higher pressure directly into the combustion chamber and has a swirl disc to get the fuel swirling as it exits the nozzle.Categories
- Manuals Home
- Kia Stinger Owners Manual
- Kia Stinger Service Manual
- New on site
- Most important about car
Contents
Copyright © 2026 www.kstinger.com 0.0076


